To submit a sitemap in Google Search Console:
- Sign in to your Google Search Console account.
- On the left-hand menu, click on “Sitemaps” under the “Indexing” section.
- In the “Add a new sitemap” field, enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g.,
https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml). - Click “Submit”.
Your sitemap will now be submitted to Google for indexing!
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages, posts, and other content on your website to help search engines like Google understand the structure of your site. It serves as a roadmap for search engine crawlers, ensuring they can easily find and index all your pages.
Having an updated sitemap is crucial for SEO because it helps search engines discover and index your content faster, improving the chances of your pages ranking higher in search results. It also ensures that all pages, including new or updated ones, are included in search engine indexes.
In WordPress, plugins like Rank Math, Yoast SEO, and All in One SEO simplify sitemap generation. These tools automatically create and update your sitemap, so you don’t have to manually add pages every time you make changes to your website.
Once your sitemap is ready, Google Search Console plays a vital role in indexing your website. By submitting your sitemap through Google Search Console, you help Google crawl and index your content more efficiently, leading to better visibility in search results.
Purpose of a Sitemap
The main purpose of a sitemap is to make sure search engines like Google can efficiently find and index all the important pages of a website. By providing a detailed list of all pages, a sitemap ensures that no content is missed, especially for large websites or those with new pages that may not be easily discovered through regular crawling.
Difference Between XML and HTML Sitemaps
XML Sitemap:
- Designed for search engines: XML sitemaps are intended primarily for search engines, helping them easily understand the structure of the site and crawl its pages more efficiently.
- Contains metadata: Includes information like last updated date, page priority, and frequency of updates, which help search engines understand the importance and relevance of each page.
- Not for users: XML sitemaps aren’t meant to be user-facing but are submitted to search engines through platforms like Google Search Console.
HTML Sitemap:
- Designed for users: HTML sitemaps are intended for human visitors to navigate a website more easily. They provide a clear, organized layout of the pages on the site.
- No metadata: Unlike XML sitemaps, HTML sitemaps are simple, clickable links that help users find pages on your site.
| Feature | XML Sitemap | HTML Sitemap |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | For search engines to crawl and index website content. | For users to navigate and find content on the website. |
| Audience | Primarily search engines (Google, Bing, etc.). | Primarily website visitors (users). |
| Format | XML (Extensible Markup Language). | HTML (HyperText Markup Language). |
| Content | Lists URLs with metadata (last updated, priority, etc.). | Lists URLs with clickable links for easy navigation. |
| Submission | Submitted to search engines via tools like Google Search Console. | Displayed on the website for users. |
| Metadata | Includes additional info such as priority, frequency, and last modified date. | Simple links with no metadata. |
| User-Friendliness | Not meant for users; only readable by search engines. | Meant for users; helps in easy navigation. |
| Impact on SEO | Helps search engines discover and index content faster. | Does not directly impact SEO but improves user experience. |
Why Search Engines Need a Sitemap for Better Crawling and Indexing
Search engines use crawlers (also known as bots) to browse the internet and find new content. A sitemap helps search engine bots by:
- Providing a clear list of pages: It helps bots discover pages that may be difficult to find through regular crawling, especially for larger websites with complex structures or pages that are not linked well.
- Speeding up indexing: With a sitemap, search engines can quickly index the important content, ensuring that it appears in search results.
- Improving website visibility: By submitting a sitemap, you ensure that all relevant pages are discovered and included in search engine indexes, boosting the website’s chances of ranking higher.
Enabling Sitemap in Rank Math, Yoast SEO, and All in One SEO
Here’s a simple guide for enabling sitemaps in these popular SEO plugins for WordPress:
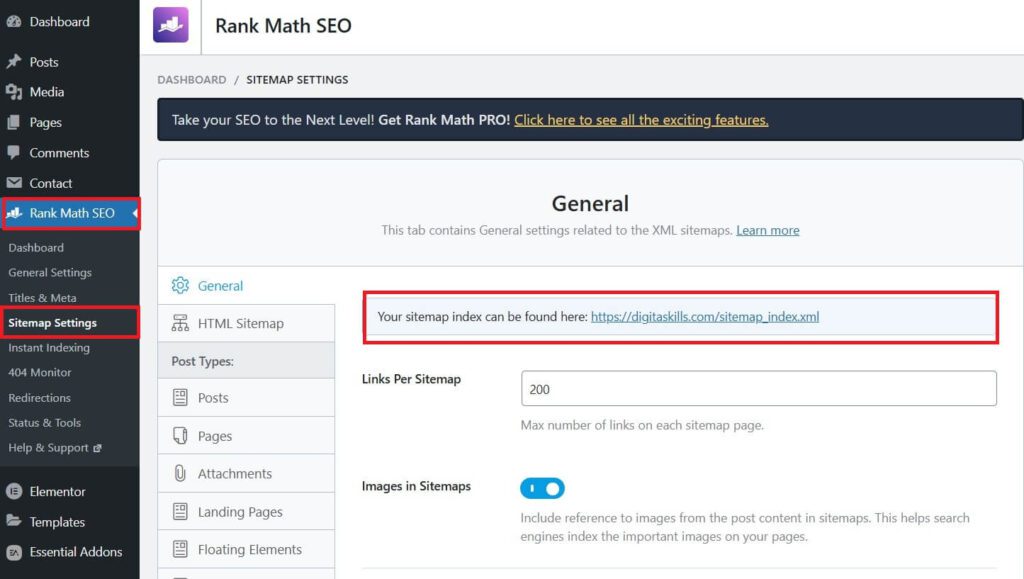
Rank Math
- Install and Activate Rank Math Plugin if not already done.
- In your WordPress dashboard, go to Rank Math > Dashboard Settings.
- Find Sitemap tab.
- Toggle the Sitemaps to Enable.
- Now go to Sitemap Settings tab.
- Customize the settings if needed, like including/excluding specific post types, taxonomies, or categories.
- Once done, Rank Math automatically generates the sitemap. You can view it by visiting
https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap_index.xml.
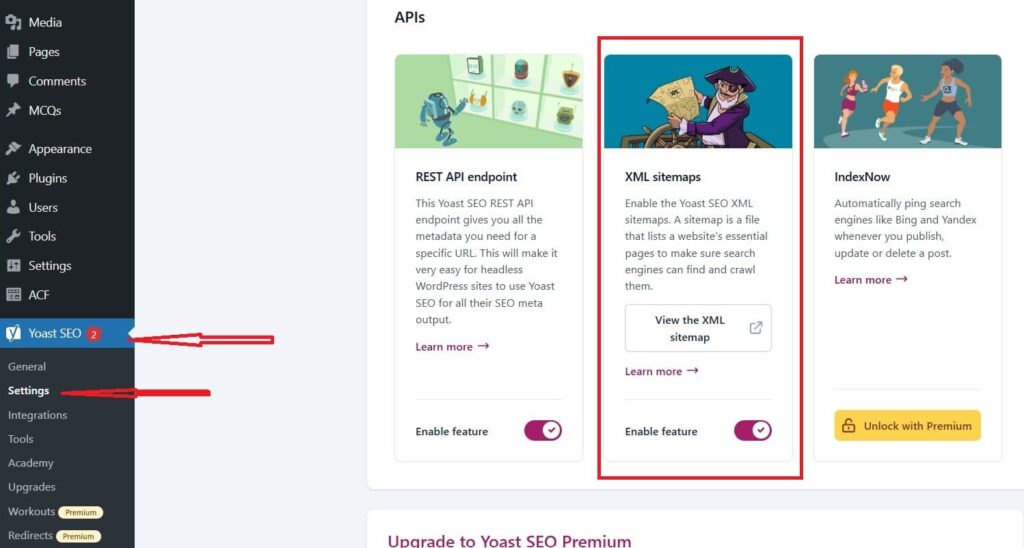
Yoast SEO
- Install and Activate Yoast SEO Plugin if you haven’t already.
- Go to Yoast SEO > Settings in your WordPress dashboard.
- Click on the Features tab.
- Enable the XML Sitemaps toggle.
- To view the sitemap, click on the question mark icon next to the toggle and then click the “See the XML sitemap” link, or simply visit
https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap_index.xml.
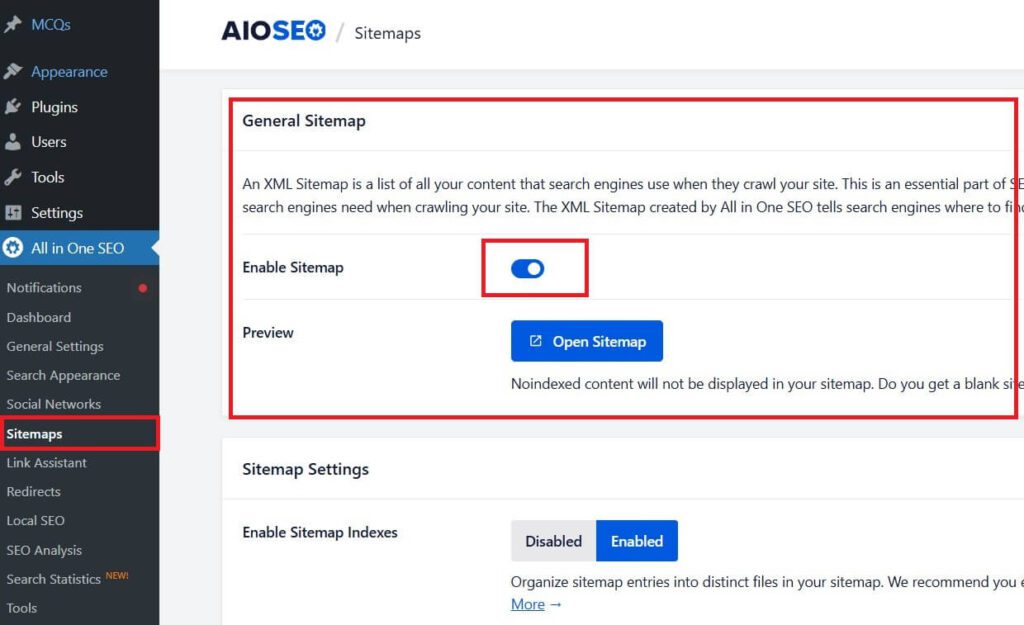
All in One SEO
- Install and Activate All in One SEO Plugin.
- Go to All in One SEO > Sitemaps in your WordPress dashboard.
- Toggle the Enable Sitemap option to On.
- Customize any additional settings, such as which post types or taxonomies to include.
- Your sitemap will be ready, and you can view it by visiting
https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml.
Finding Your Sitemap URL
Once you’ve enabled the sitemap in plugins like Rank Math, Yoast SEO, or All in One SEO, you can easily find the sitemap URL. Typically, the URL will be in the following format:
- Rank Math:
https://yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml - Yoast SEO:
https://yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml - All in One SEO:
https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml
Just replace yourdomain.com with your actual website domain.
In most cases, the default sitemap URL is structured as sitemap_index.xml for multi-sitemap plugins (like Rank Math and Yoast), or simply sitemap.xml for plugins like All in One SEO.
How to Verify if the Sitemap is Working Correctly
- Manually Check:
After finding your sitemap URL (e.g.,https://yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml), open it in a web browser. You should see a page with a list of URLs from your website. This confirms the sitemap is being generated correctly. - Google Search Console:
- Sign in to your Google Search Console account.
- Go to Indexing > Sitemaps.
- Under Add a new sitemap, enter your sitemap URL and click Submit.
- Google will notify you if there are any errors or issues with your sitemap.
- Use an Online Sitemap Checker:
You can use online tools like XML Sitemap Validator to check if the sitemap is formatted correctly and working. - Check for Errors:
If the sitemap doesn’t load or there are errors, make sure the sitemap settings in your SEO plugin are enabled, and ensure your website is accessible. You can also check for caching issues or conflicts with other plugins that might prevent the sitemap from updating.
Verifying Sitemap Submission & Troubleshooting
How to Check if Google Has Successfully Processed the Sitemap
- Google Search Console:
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Go to the Indexing section on the left sidebar and click on Sitemaps.
- Under Submitted Sitemaps, you’ll see the status of your submitted sitemap. If the sitemap is processed successfully, you’ll see the status as Success along with the number of URLs discovered.
- If there’s an issue with your sitemap, you’ll see an error or warning icon, and clicking on it will provide more details about the issue.
- Checking for Errors:
- Google will display specific errors related to your sitemap submission. Common errors include “Couldn’t fetch,” “404 Not Found,” or “Redirect error.”
- If there are no issues, your sitemap will be marked as Success, and Google will start crawling your website accordingly.
Common Sitemap Issues & How to Fix Them
- “Couldn’t Fetch” Error:
- Cause: Google could not access the sitemap file due to server errors or incorrect permissions.
- Solution:
- Check if the sitemap URL is correct (make sure there’s no typo).
- Ensure the sitemap file is publicly accessible.
- Check server logs for any server-side issues (timeouts, missing files, or security restrictions).
- If you’re using a cache plugin, clear the cache and try again.
- Check your robots.txt is correct or not
Here is my robots.txt
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
Sitemap: https://digitaskills.com/sitemap_index.xml- 404 Not Found Error:
- Cause: The sitemap URL is incorrect, or the file is missing.
- Solution:
- Double-check the sitemap URL and ensure it is active (e.g.,
yourdomain.com/sitemap_index.xml). - Re-submit the correct sitemap URL in Google Search Console.
- If the sitemap is generated dynamically, ensure your SEO plugin is functioning properly.
- Double-check the sitemap URL and ensure it is active (e.g.,
- Redirect Error:
- Cause: The sitemap URL is redirecting to another page, which prevents Google from accessing it.
- Solution:
- Ensure the sitemap URL doesn’t redirect to another page (use the correct sitemap URL in your SEO plugin settings).
- Check for issues like redirects or broken links in your website’s .htaccess file or server settings.
- Large Sitemap File or Too Many URLs:
- Cause: Google cannot process a very large sitemap file or one with an excess of URLs.
- Solution:
- Split the sitemap into multiple files if it exceeds Google’s size limit (50,000 URLs or 50MB per file).
- Use sitemap index files to point to multiple smaller sitemaps.
- Ensure all URLs are in a readable format and follow Google’s guidelines.
Importance of Keeping the Sitemap Updated
- Reflect New Content:
- As you add new pages, blog posts, or products to your website, make sure your sitemap is updated to include them. This allows search engines to discover and index your new content quickly.
- Most SEO plugins like Rank Math, Yoast SEO, and All in One SEO automatically update the sitemap when new content is added. Ensure the plugin’s settings are correctly configured for auto-updates.
- Removing Content:
- If you remove pages or posts from your website, update your sitemap to reflect these changes. This helps prevent search engines from crawling deleted or outdated pages, ensuring they don’t get indexed by mistake.
- Some SEO plugins automatically update the sitemap when content is removed, while others may require you to manually remove certain pages from the sitemap.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Even if your sitemap is updated automatically, it’s important to regularly check Google Search Console for any issues or crawling problems.
- Keeping your sitemap updated ensures that Google has accurate information about your site, which can improve crawling efficiency and SEO performance.
Benefits of Submitting a Sitemap
1. Faster and Better Indexing
- Why it matters: Submitting a sitemap allows Google to crawl your website more efficiently, ensuring that all pages are indexed faster. When you submit a sitemap, you essentially give Google a roadmap of your site, making it easier for the search engine to find and index content, including pages that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Impact: This results in quicker visibility for new pages or updates, helping your content to show up in search results sooner.
2. Improved SEO and Search Rankings
- Why it matters: When search engines can crawl your entire site and index all pages correctly, it improves your site’s overall SEO performance. By submitting a sitemap, you ensure that all important pages (including those that might be buried deep within your site) get discovered and indexed.
- Impact: With better crawlability and indexing, your site has a higher chance of ranking well in search engine results, improving your organic traffic and online visibility.
3. Helps Google Understand Site Structure
- Why it matters: A sitemap outlines the hierarchy and relationships between pages on your website. This makes it easier for search engines like Google to understand how your site is organized and prioritize important pages.
- Impact: A clear site structure helps Google crawl and rank pages based on their relevance and importance, which can lead to better search rankings and more accurate indexing of your content.
How to Delete a Sitemap in Google Search Console
- Log in to Google Search Console
Open your browser and go to Google Search Console. Log in using your Google account. - Select the Property (Website)
Choose the property (website) from which you want to delete the sitemap. - Go to the Sitemaps Section
In the left-hand menu, click on “Sitemaps” under the “Index” section. - Find the Sitemap to Delete
You’ll see a list of submitted sitemaps under the “Submitted Sitemaps” section. Find the sitemap you wish to remove. - Click the Three Dots (More Options)
Next to the sitemap you want to delete, click on the three dots (ellipsis) on the right side of the row. - Click “Remove”
In the dropdown menu, select “Remove”. This will delete the sitemap from Google Search Console.Note: Deleting the sitemap from Google Search Console does not remove the actual sitemap from your website. You will still need to remove the sitemap file from your server or CMS (like WordPress) if you no longer want it to be available. - Confirm Removal
Once deleted, the sitemap will no longer be listed in Google Search Console, and Google will stop using it for crawling.
Important Points:
- Removing the Sitemap in Search Console doesn’t delete the sitemap file from your website. You’ll need to delete the actual file from your server or CMS if it’s no longer needed.
- Google will continue to crawl your site even without the sitemap, but it might be slower and less efficient without it.
Conclusion
Sitemaps are an essential tool for improving your website’s SEO. They act as a guide for search engines, making it easier for them to crawl, index, and understand the structure of your site. By submitting your sitemap to Google Search Console, you ensure that your website’s content is discovered quickly, indexed efficiently, and properly ranked in search engine results.
Regularly monitoring your sitemap status is crucial to ensure that Google has up-to-date information about your site. It helps identify and resolve any crawling or indexing issues, allowing you to maintain a healthy SEO profile. Keep your sitemap updated, and make sure all content is reflected accurately to improve your search rankings and visibility.
FAQ: Sitemap Submission and Google Search Console
Do I need to submit a sitemap for every website?
While not mandatory, submitting a sitemap is highly recommended for all websites, especially larger sites with complex structures. It helps search engines crawl your website more efficiently and ensures that all your pages, including new or hidden ones, are indexed.
Can I submit multiple sitemaps for one website?
Yes, you can submit multiple sitemaps for a single website. This is especially useful for large websites with many pages. For instance, you can split your sitemap into categories (e.g., blog pages, product pages) and submit them all under one sitemap index file.
What happens if I don’t submit a sitemap in Google Search Console?
If you don’t submit a sitemap, Google will still try to crawl your website, but it may take longer to index your pages. In the absence of a sitemap, some pages might be missed, especially those deep within the site or with low internal links. A sitemap makes it easier and faster for search engines to crawl and index your content.
How do I update my sitemap in Google Search Console?
If you’ve made changes to your website or added new content, the sitemap will update automatically if you’re using a plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math. After updating the sitemap, go to Google Search Console, navigate to the Sitemaps section, and input the URL and click Submit to ensure Google crawls the updated sitemap.
Can I submit a sitemap for a website with no content yet?
Yes, you can submit a sitemap even if your website doesn’t have much content yet. This helps Google to start indexing your site as soon as content is available, and it can make the process quicker when new content is added. However, it’s best to wait until you have some substantial pages or posts live before submitting a sitemap for better results.



